The 1000L Fibreglass Olive Pickling Tank is designed specifically for table olive fermentation and curing. Widely used in major olive-producing countries, this tank provides reliable performance with food-grade construction, easy handling, and long-term usability. Its convex bottom and fitted outlets make it efficient for draining brine and olives during processing.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Capacity | 1000 L |
| Material | Food-grade fibreglass |
| Legs | 3 legs, 300mm (taller optional) |
| Outlets | 2" brine pipe (63mm), 4" olive pipe (110mm) |
| Top Opening | 800mm with lid |
| Body Thickness | 6mm |
| Interior Colour | Black |
| Exterior Colour | White |
| Dimensions | 1.056m diameter, 1.85m height |
This 1000L fibreglass pickling tank provides olive processors with a reliable solution for curing and fermentation. The convex bottom design supports efficient drainage, while the fitted outlets simplify brine and olive transfers. With FDA-suitable fibreglass and easy-to-clean surfaces, it helps producers maintain hygiene and quality across each batch. Built for commercial use, it is a trusted choice in major olive-growing regions.
Q: What makes fibreglass tanks effective for small to medium-scale olive pickling?
Table olive curing requires stable containers that resist brine corrosion, maintain hygiene, and provide efficient drainage. Traditional containers can cause uneven fermentation or be difficult to clean, leading to inconsistent results and wasted product. Fibreglass tanks overcome these issues by offering a smooth, non-reactive surface that withstands brine and simplifies maintenance.
The 1000L size is particularly suited for small to medium-scale operations, providing enough capacity for commercial use without excessive space requirements. Its convex bottom and dual outlet pipes allow for efficient transfer of brine and olives, while the raised legs provide stability and clearance for handling. This combination supports consistent fermentation cycles and better workflow in curing facilities.
Key advantages include:
The result is improved batch consistency, reduced product loss, and greater efficiency in table olive curing and fermentation.

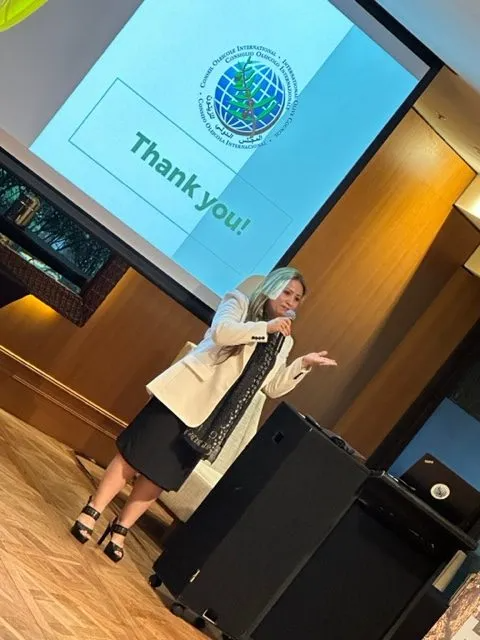
Sydney, Australia — October 20: In recent days, Sydney welcomed a delegation from the International Olive Council, comprising Maria Juarez, Head of Promotion and Economic Affairs; Dr. Imene Trabelsi Trigui, Head of Promotion; and Dr. Wenceslao Moreda, Principal Scientist and IOC specialist.
Their visit was intended to deliver a program of events in Sydney, including a two-day technical tasting workshop and a formal networking cocktail reception.
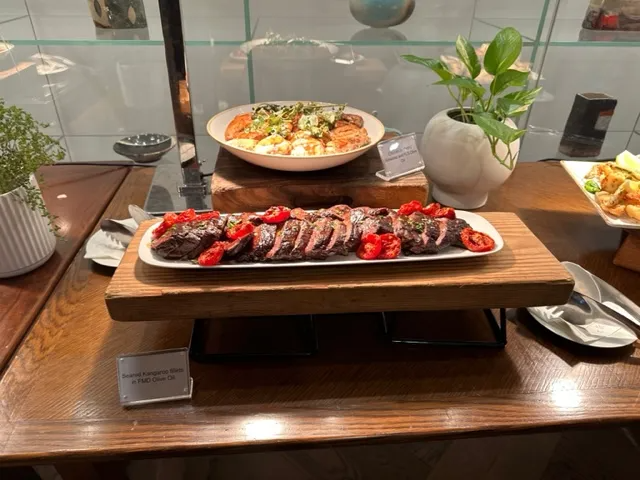
The objectives of these events were twofold. The workshop sought to strengthen collaboration between Australian growers, producers, and the International Olive Council, while the networking cocktail reception united key stakeholders — including government officials, media representatives, chefs, and producers — in a dynamic exchange. A highlight of the evening was the introduction of the newly appointed Ambassador, Mark Olive, who captivated guests with a specially crafted menu featuring Australian Indigenous ingredients such as saltbush, kangaroo, bush tomato, and native peppers, elegantly paired with a selection of Australian Extra Virgin Olive Oils.
“Advancing sustainability in olive oil production is essential to tackling climate change. We encourage producers to embrace sustainable methods that not only reduce environmental impact but also help optimize production costs. Australia’s strengthened partnership with the IOC represents a step toward a healthier and more sustainable future. Our mission is to promote greater awareness of olive oil’s benefits and sustainable practices, fostering improved and healthier consumption.” — Dr. Imene Trabelsi, Head of Promotions, International Olive Council
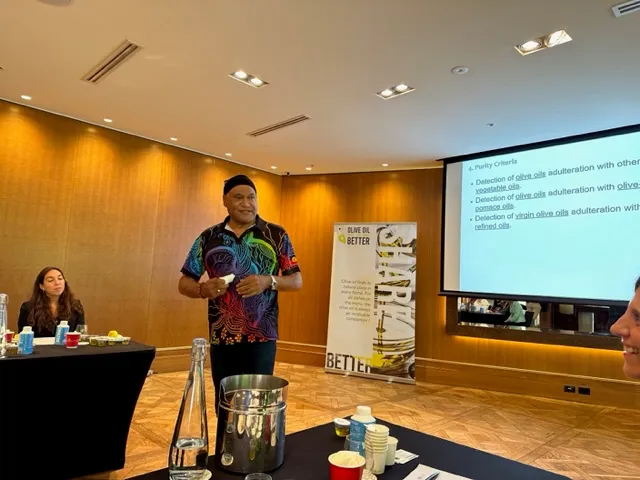







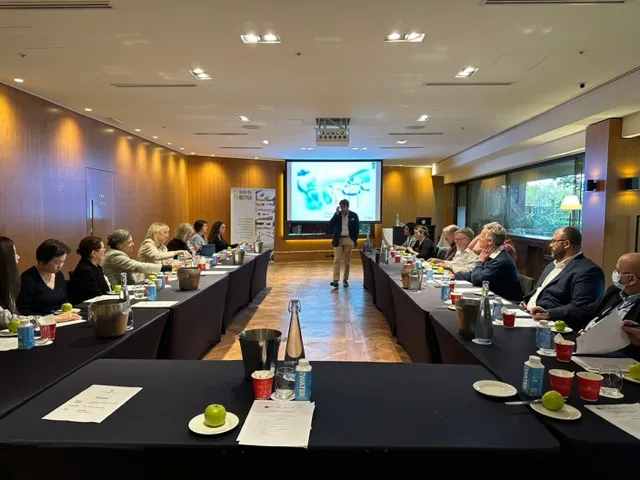
The two-day technical workshop was led by Dr. Wenceslao Moreda, an IOC specialist and Chair of the eWG of the Codex Committee on Fats and Oils (CCFO). A distinguished member of the Spanish National Research Council, Dr. Moreda holds an impressive record of over 75 research publications dating back to 1995. The opening day of the workshop focused on sensory evaluation, addressing both the physical and psychological dimensions of the organoleptic process while emphasizing the importance of proper production conditions in compliance with the rigorous standards established by the International Olive Council. The discussions provided valuable insight into the rationale behind these standards and the allowances for specific variances, reinforcing their role as the overarching global benchmark.
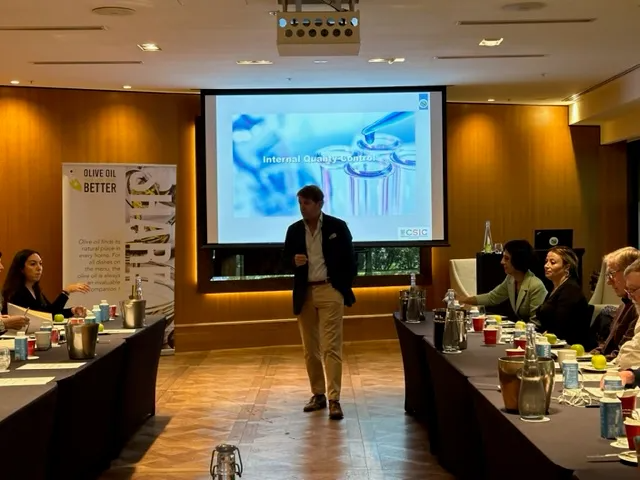



On the second day, the workshop focused on the quality and purity of Extra Virgin Olive Oil, examining internal quality control measures and evaluation criteria. The program concluded with an in-depth review of health-related parameters associated with olive oil, attended by nutrition experts. The breadth of technical knowledge shared proved highly valuable, offering participants a holistic understanding of the journey from production to final product from an organoleptic perspective. During the session, the IOC also announced the development of a new website dedicated to communicating the extensive health benefits of olive oil.
The International Olive Council continues to be a steadfast leader in shaping the global olive oil sector, establishing standards and fostering international collaboration essential to the industry’s advancement. As these remarkable events draw to a close, they leave a lasting impression of unity, progress, and shared commitment to the treasured ‘liquid gold’—extra virgin olive oil.
Beyond celebrating the richness and versatility of olive products, these gatherings underscored the critical importance of cooperation and knowledge exchange within the global olive community.
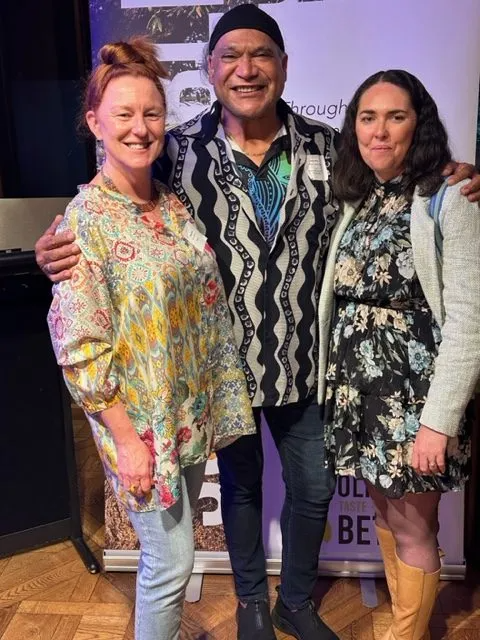
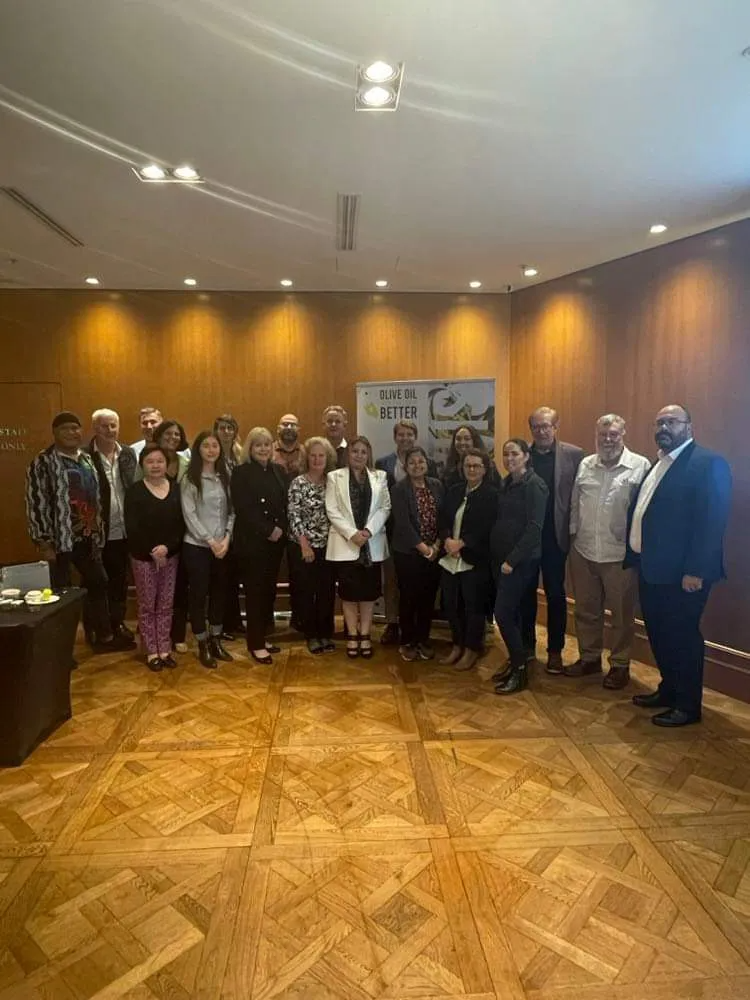





The International Olive Council (IOC) functions as the leading intergovernmental organization responsible for establishing the regulatory framework governing the global olive oil sector. Although Australia is not yet an official IOC member, it actively supports the organization by assisting emerging industries in adopting and applying international standards. The cooperation demonstrated during recent events underscored the IOC’s global significance and lasting impact.
The IOC also recognizes the diversity of growing conditions worldwide, which may lead to parameter variations outside of established guidelines in certain producing regions. Importantly, the IOC administers the only legally binding international standard for olive oil, reinforcing its critical role from a legislative and regulatory perspective. Complementing this, the Australian Olive Oil Association (AOOA) is acknowledged for its collaborative work with the IOC, further highlighting the importance of sustained international cooperation within the sector.
IOC Membership Process
The International Olive Council maintains strict criteria for membership. Participation is reserved exclusively for governments or international organizations empowered to negotiate, conclude, and implement international agreements, particularly those relating to commodities.
When a country seeks to join the IOC, its government must formally apply to the Council of Members, typically through its Ministry of Foreign Affairs, another relevant ministry, or its Embassy in Spain. The Council then reviews the application, establishes terms and conditions of accession — including financial contributions to the IOC budget — and sets a deadline for depositing the instrument of accession with the Secretary-General of the United Nations in New York, who serves as the official depository of the Agreement.
Upon successful deposition, the applicant nation becomes a full IOC Member. Private companies and individuals are not eligible for membership. Additionally, all European Union Member States are automatically represented in the IOC through the EU’s membership, without the need for separate applications.
In Australia’s case, stronger collaboration between national associations, government agencies, and the IOC will be essential for achieving closer alignment with international standards. Leadership from within the Australian olive oil industry itself will be critical in driving forward discussions on potential membership.
IOC Health Website
The IOC has recently launched a new website serving as a comprehensive reference hub on olive oil and health.
IOC Standards, Methods, and Guidelines
The IOC continues to provide the latest updates on trade standards for olive oil and table olives, as well as official testing protocols, sensory (organoleptic) assessment methods, and quality management practices.
In the pursuit of advancing olive oil quality, a groundbreaking development for the industry has emerged from a recent study that has illuminated how specific compounds — particularly secoiridoids — can substantially improve the oxidative stability and shelf life of ‘Corbella Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO).
The collaborative Spanish study, carried out at an industrial mill, centered on assessing the influence of malaxation conditions and olive storage on the composition of ‘Corbella’ EVOO, offering insights with potentially transformative implications for the sector.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil is celebrated worldwide for its health-promoting properties and distinctive flavor, establishing itself as a culinary cornerstone across cultures. Nevertheless, its oxidative stability — a key factor in determining shelf life and overall quality — has long been the focus of intensive research. This latest investigation has presented compelling evidence that certain compounds play a decisive role in reinforcing EVOO’s stability.
The principal compounds examined included phenolic compounds, tocopherols, carotenoids, squalene, and fatty acids, all of which are fundamental to the oil’s composition. The findings revealed that extended malaxation at higher temperatures, together with olive storage, negatively affected compounds such as α-tocopherol, squalene, flavonoids, lignans, phenolic acids, and phenolic alcohols. However, paradoxically, both the antioxidant capacity and oxidative stability of the oil improved under these conditions. This enhancement was attributed to a marked increase in the concentration of two secoiridoids: oleacein (56–71%) and oleocanthal (42–67%).
Oleacein and oleocanthal are widely recognized for their potent antioxidant activity, and this study has underscored their critical contribution to reinforcing EVOO’s stability and extending its shelf life. In addition, the research identified a synergistic interaction between secoiridoids and carotenoids, further highlighting their collective role in enhancing the resilience and longevity of EVOO.
Concentrations (mg/kg oil) of squalene, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, lutein, secoiridoids, oleacein, and oleocanthal in ‘Corbella’ Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) samples O1 and O4, along with the oleic/linoleic ratio, antioxidant capacity (DPPH, µg TE/g oil), and oxidative stability (Rancimat induction time, h). Sample O1 was produced on the day of harvest, while O4 was produced the following day using stored olives. Both EVOOs were malaxed at 18 °C for 30 minutes. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 9). All parameters showed significant differences (p < 0.05) between samples.
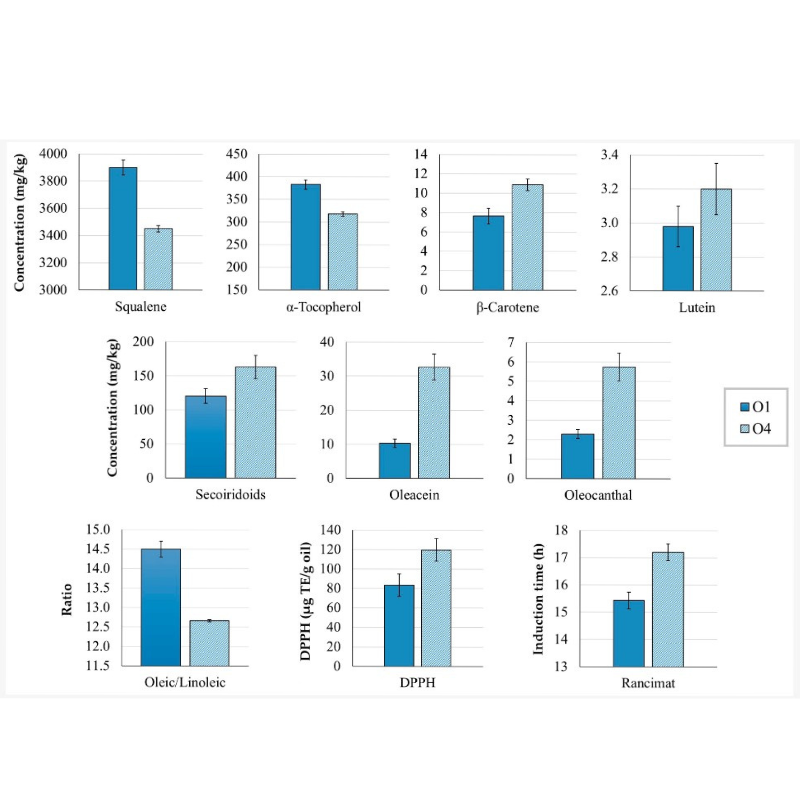
One of the most notable discoveries was the ‘Corbella’ cultivar’s ability to yield EVOOs with a favorable oleic/linoleic ratio. The research indicated that storing olives overnight at ambient temperature, followed by malaxation at no less than 23 °C for 40–50 minutes (depending on the precise temperature), could substantially elevate the concentrations of oleacein and oleocanthal. This increase, in turn, contributed to a measurable improvement in the oxidative stability of EVOOs.
These findings represent a significant advancement in efforts to address and enhance EVOO stability, offering practical applications for producers aiming to extend shelf life while safeguarding quality.
The study also highlighted several promising avenues for future research. Key areas of interest include identifying strategies to further elevate oleacein and oleocanthal levels through agronomic and climatic variables, fruit maturity, and technological aspects of oil extraction.
Moreover, the evaluation of EVOO quality and stability over long-term storage, together with interventional studies assessing the direct influence of these secoiridoids on both product longevity and human health, remains a critical area requiring deeper exploration.
In summary, the research underscores the pivotal role of secoiridoids — particularly oleacein and oleocanthal — in enhancing oxidative stability and extending the shelf life of ‘Corbella’ EVOO. These insights hold dual significance: they offer tangible benefits for producers while also presenting potential health advantages for consumers, marking a milestone in the olive oil industry’s ongoing pursuit of excellence.
Research conducted by Alexandra Olmo-Cunillera 1,2ORCID,Maria Pérez 1,2ORCID,Anallely López-Yerena 1ORCID,Mohamed M. Abuhabib 1ORCID,Antònia Ninot 3ORCID,Agustí Romero-Aroca 3ORCID,Anna Vallverdú-Queralt 1,2ORCID andRosa Maria Lamuela-Raventós
About Secoiridoids
Secoiridoids exhibit a wide range of pharmacological properties, including anti-diabetic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, neuroprotective, anti-cancer, and anti-obesity effects. These diverse biological activities have significantly heightened scientific interest in the in-depth study of these bioactive compounds.
About Olive Oil Processing Technologies
Olive Oil Processing Plants: Compact Olive Oil Processing Machinery, Processing Lines from 500kgs/hr – 10T/hr & Specialised Machinery to Enhance Your Line
Processing Articles
INDUSTRY UPDATE: AUSTRALIAN OLIVE GROWERS 2023 SEASON

“Earlier in the season, the industry was anticipating an excellent harvest,” Mr Valmorbida said. “However, persistent cold weather and rainfall during May and June, particularly across south-east Australia, have taken their toll.”
Although the Australian olive harvest is not officially recorded each year, the AOOA estimates that the 2023 season will produce between 18 and 19 million litres of olive oil from roughly 110,000 to 120,000 tonnes of olives.
This compares with last year’s output of 14–15 million litres and the record-breaking 2021 crop, which yielded 20–22 million litres of oil.
Mr Valmorbida explained that these fluctuations reflect the biennial cycle of olive production. “This is what we call an ‘on’ year for olives. While we were expecting an excellent yield earlier in the year, harvest results always depend heavily on weather conditions, and this season has been quite mixed for many growers.”
“The oil yield per tonne is noticeably lower than average due to the cooler growing period,” he added, “but the quality of the oil remains excellent because the fruit had more time to ripen gradually.”
Around the world, olive oil prices have reached record highs in Spain, Italy, and Greece, driven by a severe global shortage of olive oil. Hot temperatures, minimal rainfall during key stages of the growing season, and extended drought conditions across southern Spain have drastically reduced European output. In addition, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has disrupted the production of vegetable and seed oils, increasing global demand for olive oil as an alternative.
In Australia, growers are currently achieving $6–$7 per litre for larger commercial volumes of olive oil, with even higher prices for export batches, premium small-lot oils, and organic extra virgin olive oil.
“With this global shortage, some of the larger Australian producers are in a strong position to export olive oil to Europe and receive competitive returns,” Mr Valmorbida said.
“While that’s encouraging news for the Australian olive oil industry, globally the sector is under pressure,” he continued. “There’s currently a 35–40 percent shortfall in available products, combined with escalating packaging costs, especially for glass and tin materials.”
“These factors, along with rising labour and energy expenses, are leading to higher retail prices for consumers,” he noted.
Mr Valmorbida concluded with a reminder to consumers: “It’s important to remember there’s no product quite like olive oil—its distinctive flavour, health benefits, and culinary versatility make it irreplaceable.”
#oliveharvest2024 #harvest2024
The Australian Olive Oil Association (AOOA) is a not-for-profit, independent organisation dedicated to promoting the quality, integrity, and fair trade of olive oil in Australia. Membership is open to olive oil producers, distributors, industry stakeholders, and related organisations.
Since 1993, AOOA has been a signatory to the International Olive Council (IOC) global quality control program. Each year, the Association coordinates independent laboratory testing of leading olive oil brands to ensure compliance with IOC standards.
In addition, the AOOA Certified Quality Seal Program upholds even stricter quality criteria, allowing AOOA-member products to distinguish themselves in both domestic and international markets.
For more information:
Jan Jacklin, General Manager, Australian Olive Oil Association gm@aooa.com.au www.aooa.com.au
Photo credit: Julia, olive grove – Kyneton Olives” by avlxyz is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0. To view a copy of this license, visit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/?ref=openverse
MARKET INSIGHT: GLOBAL OLIVE OIL ECONOMY 2023
Introduction
The global olive oil industry in 2023 has entered uncharted territory, experiencing an extraordinary surge in olive oil prices driven by a combination of climatic and economic forces. At the centre of this crisis lies Spain’s devastating drought, which has crippled the world’s largest olive oil producer. This severe shortage has led to a dramatic contraction in olive oil supply, triggering price escalation and a corresponding decline in consumer demand. The ripple effects are being felt worldwide, reshaping the balance between producers and consumers alike. Meanwhile, Australian olive oil producers find themselves in a rare position of advantage, benefitting from unprecedented market highs. This article explores the causes, consequences, historical trends, and economic signals surrounding this remarkable global olive oil price spike.
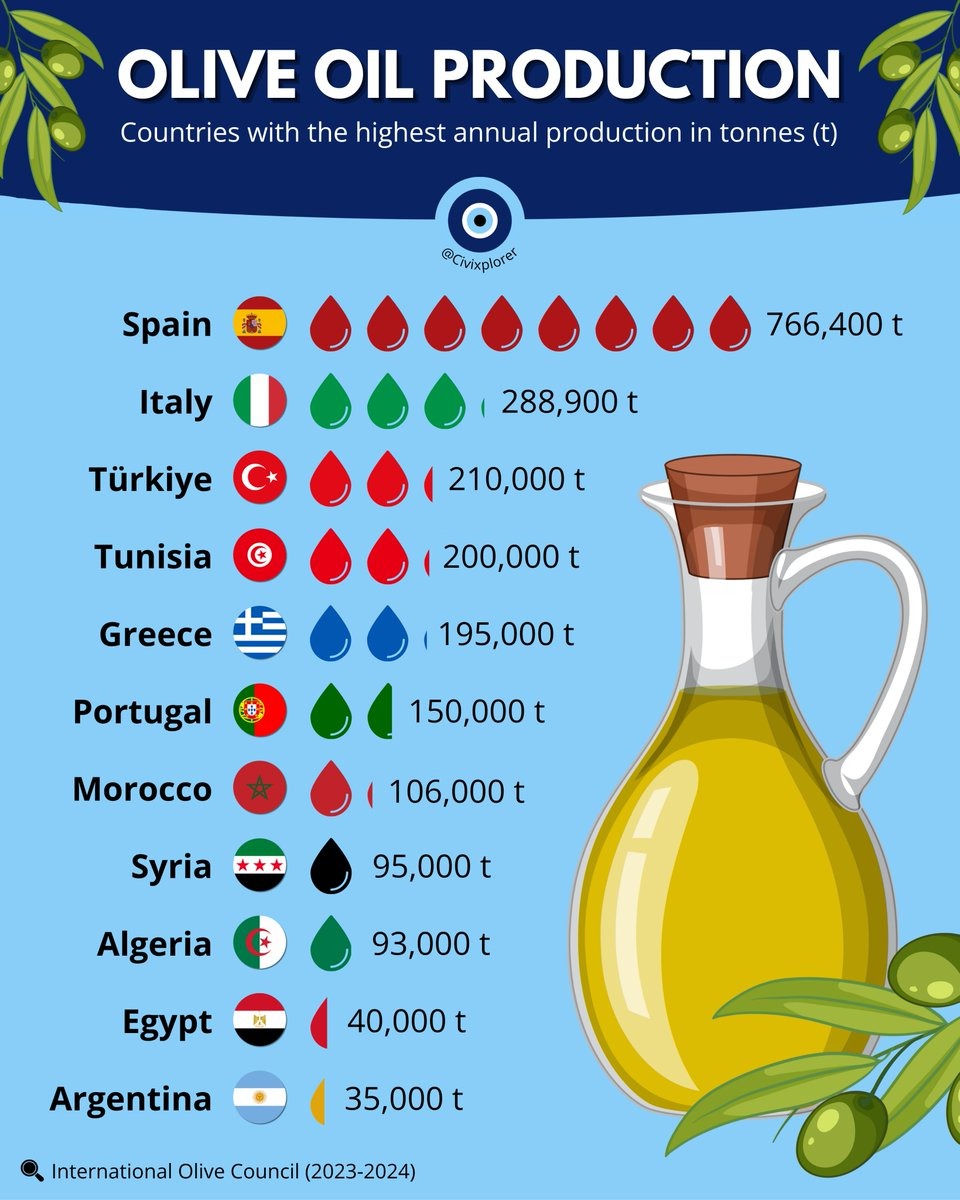
The ongoing drought across Spain stands as the principal factor behind the current olive oil price surge. As one of the largest olive oil-producing nations globally, Spain’s drastically reduced harvest - caused by months of extreme heat and minimal rainfall - has sharply curtailed olive oil availability in both European and international markets. This has intensified supply shortages, compelling consumers to pay more for what has long been a staple Mediterranean product. The interplay of limited supply and escalating demand has magnified price volatility, reinforcing the classic supply-and-demand imbalance now driving global markets.
Incredible to see the olive groves of Jaen, Spain. This one province produces around a fifth of the *entire* global supply of olive oil
— Secunder Kermani (@SecKermani) August 31, 2023
But a combination of drought & extreme heat has left many trees badly weakened... This years harvest looks set to be the worst in living memory pic.twitter.com/QYs41eXCwC
As prices have risen steeply, the shortage of olive oil has led to a noticeable decline in consumption, particularly in Spain, where demand has reportedly dropped by around 35%. Consumers are now scaling back their purchases, finding olive oil increasingly unaffordable compared to other cooking oils. The once-steady household consumption patterns are shifting as people seek alternatives or modify their cooking habits. This contraction in domestic demand not only highlights the growing accessibility gap for consumers but also underscores the broader economic strain caused by high inflation and food price increases.
Amid the turmoil, Australian olive oil producers are experiencing a windfall. Thanks to limited global supply, Australian growers are commanding record prices exceeding AUD $8 per litre, marking the highest levels ever recorded in the nation’s olive oil industry. This lucrative period presents a rare opportunity for Australian exporters, with demand from Europe - including Spain itself - now turning toward Australian supplies. For producers Down Under, this unique reversal of roles underscores how regional climate resilience and diversified production can translate into significant financial gains when global shortages arise.
The olive oil market’s volatility is not a new phenomenon. Previous spikes occurred in 1996, 2006, and 2015, each triggered by weather-related supply constraints. Yet, the 2023 price explosion stands out as the most dramatic in recorded history -over 40% higher than any previous price peak, and roughly double the magnitude of earlier surges. This extreme escalation reflects not just climatic hardship but a clear pricing bubble forming within the market, echoing the cyclical nature of commodity pricing.
The olive oil sector has long followed cyclical pricing patterns, typically alternating between low and high price phases roughly every decade. The current surge aligns almost perfectly with the predicted start of another 10-year cycle, occurring just three years into its anticipated timeline. Furthermore, a notable correlation has been identified between the Australian Food Inflation Index and the Global Olive Oil Price Index as reported by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). This connection illustrates the deep interdependence between food commodity pricing and global economic conditions.
While the IMF’s benchmark prices are denominated in USD, for the purposes of this analysis they have been converted to AUD to track the trend relative to Australian markets. These benchmark indicators -based on the world’s largest olive oil exporters -serve as a reliable gauge of overall market direction, confirming how global shortages and inflationary pressures move in tandem.
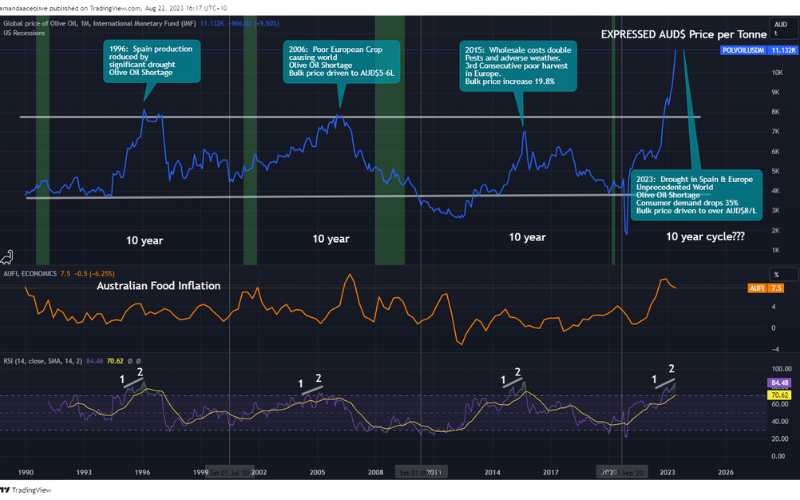 Global olive oil prices show a recurring 10-year cycle, driven by droughts, crop shortages, and rising production costs
Global olive oil prices show a recurring 10-year cycle, driven by droughts, crop shortages, and rising production costs
From a technical analysis perspective, the Relative Strength Indicator (RSI) is often used to measure price momentum and potential overextension in markets. On recent olive oil price charts, the RSI (represented in purple) indicates that prices have once again entered overbought territory - a level seen during previous speculative phases. Historically, such readings have preceded market corrections or reversals, suggesting that the current surge may not be sustainable in the long term.
Analysts caution that as the European olive harvest begins in September and October 2023, an influx of new oil supplies could help ease prices, though the timing and extent of this correction remain uncertain. Until then, speculative trading and limited inventory continue to support inflated market values.
The record-breaking olive oil prices of 2023, primarily triggered by Spain’s drought-induced production collapse, mark a turning point for the global olive oil economy. With consumer demand declining under the pressure of soaring prices and Australian producers thriving amid the scarcity, the industry is experiencing a dramatic rebalancing. Historical precedents, cyclical trends, and market indicators all point toward a complex, transitional period defined by volatility and uncertainty.
As the world’s producers, traders, and consumers adapt to these new market dynamics, one truth remains clear: olive oil - celebrated for its taste, health benefits, and cultural significance - continues to be at the mercy of both climate change and economic cycles. Stakeholders across the value chain must remain alert, flexible, and forward-thinking as the olive oil market navigates this extraordinary phase of transformation.
Other Sources