


Many configurations are available. Speak with one of our expert staff about your requirements
Click here to see our range of Oliomio olive oil machines
About the Oliomio Estate owned by the makers of Oliomio & Frantoino....
This is what started it all... the first Oliomio 50 machine ..... see the operational video.(for informational purposes only)
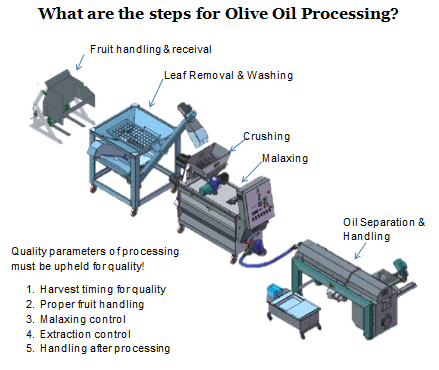
Modern extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) production relies on continuous centrifugal extraction, which has largely replaced traditional presses. In a continuous system, olives are cleaned, crushed into paste, and then malaxed (gently mixed) before a horizontal decanter centrifuge separates oil from water and solids. This process is far more efficient and hygienic than the old press-and-mat method, which is now considered obsolete. Key quality factors include processing fruit quickly to avoid fermentation, maintaining low temperatures during malaxation, and minimising exposure to oxygen. For example, transporting olives in ventilated crates and crushing/milling within 24-48 hours of harvest helps prevent heat buildup and unwanted fermentation that could spoil flavour. Cleaning and de-leafing the fruit before crushing is also critical - removing leaves, dirt, and debris ensures no off-flavours or contaminants make it into the oil. Mordern mills typically incorporate washing and leaf-removal steps for this reason.

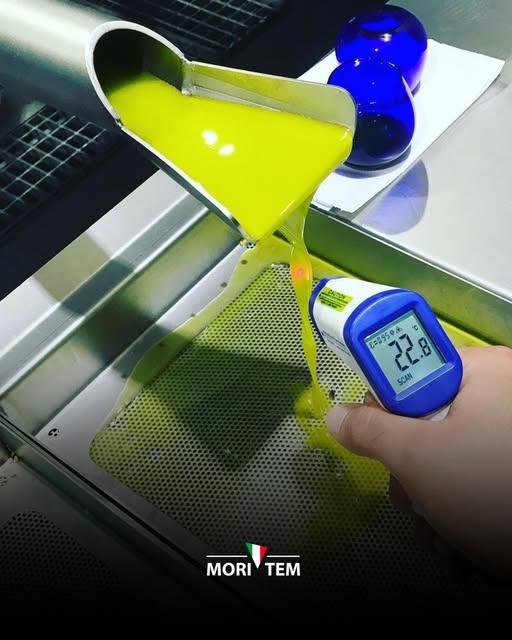
Temperature control is paramount during extraction. EVOO is generally produced under “cold-press” conditions, meaning malaxation is kept around ≤27 °C to preserve aromatic compounds and polyphenols. Longer malaxation times or higher temperatures can increase yield but will reduce polyphenol content and flavour freshness. Recent research confirms that malaxation time and temperature must be optimised per cultivar e.g., one study found that extending malaxation from 15 to 90 minutes caused polyphenols to drop by up to 70%. In Australian groves, where harvest season temperatures can be high, processors often monitor paste temperature closely and may use heat exchangers or vacuum conditions to control it. Shorter malaxation (20-40 minutes) at moderate temperatures is commonly employed to balance oil yield with quality retention. Equally important is timing from harvest - olives allowed to sit too long (especially in warm conditions) will start fermenting. Using shallow, well-ventilated bins and milling within a day of picking is recommended to keep olives cool and intact. Big Horn Olive Oil in USA, for instance, emphasises rapid processing: they cold-press olives within 2 hours of harvest to “lock in freshness and antioxidants,” drastically reducing oxidation time in between. Such practices help Australian producers achieve long shelf life (18 - 24 months) and vibrant flavour in their EVOO whereas Cockatoo Grove has a Midnight EVOO where they pick and press in the cool of the night.

Ongoing research in Australia has highlighted how harvest timing and orchard factors influence oil quality. As olives mature on the tree, oil yield rises, but phenolic compounds (antioxidants) tend to drop. In field trials across New South Wales and Victoria, early-harvest olives produced oils with higher polyphenol content and longer shelf stability, whereas late-picked fruit gave more mellow oils with lower antioxidant levels. Free fatty acidity and peroxide (rancidity indicators) remained low until fruit became overripe, but antioxidant-rich components like tocopherols and polyphenols decreased as the fruit matured, leading to reduced oxidative stability in late-season oils. Australian producers must therefore balance quantity vs quality: an early pick yields robust, pungent oils rich in healthful polyphenols, while a later pick yields more volume with milder taste. The table below (adapted from industry data) illustrates this trade-off:
| Harvest Time | Oil Yield (% by weight) | Flavor Profile | Antioxidant Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early (greener fruit) | ~12-16% (lower) | Green, grassy, intensely fruity; pronounced bitterness & pungency | High (rich in polyphenols) |
| Mid-Season | ~15-18% (moderate) | Balanced fruitiness; moderate pepperiness | Moderate |
| Late (ripe fruit) | ~20-28% (higher) | Mild, buttery, nutty; low bitterness/pungency | Lower (fewer polyphenols) |
Other local research has examined irrigation effects on oil quality. Water-stressed olive trees (common in Australian summers) often produce smaller, more bitter fruit with higher polyphenol content, whereas heavily irrigated trees yield plumper olives with diluted phenolics but higher total oil output. For example, a study found that deficit-irrigated trees had the highest polyphenol levels (and earlier fruit ripening) in dry years, while fully irrigated trees gave greater oil yields at the cost of some phenolic concentration. These findings underscore that post-harvest decisions (when to pick, how to handle fruit before milling/crushing) are just as crucial as the milling technology itself. Cutting-edge extraction equipment can maximise quality potential, but growers must still deliver quality olives to the mill and process them with urgency to produce premium Australian EVOO.

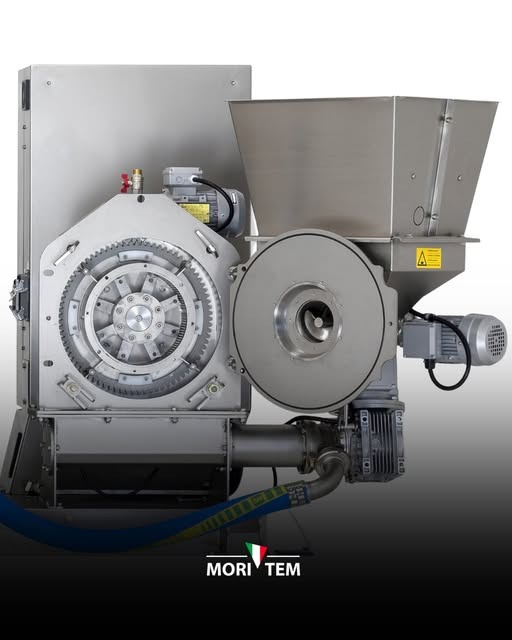
MORI-TEM offers a spectrum of Oliomio mills to suit different scales, from artisanal boutique producers up to small commercial cooperatives. All share the principles above, but with varying throughputs and degrees of automation. Below is an overview of the current Oliomio lineup and its characteristics:
To summarise the small-to-medium Oliomio models discussed above, the table below compares their capacities and key features:
| Oliomio Model | Throughput | Key Features | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spremoliva C30 | 30-40 kg/hour | Batch malaxer (discontinuous); basic mini-press setup; no built-in heating or automation | Hobbyists, micro-batch or lab use (older design) |
| Frantoino Bio | ~50-60 kg/hour | Continuous 2-phase system; single malaxer; simple controls; single-phase power; adjustable decanter nozzles | Boutique farms, artisanal producers, pilot plants |
| Oliomio 80 Plus | ~70-80 kg/hour | Continuous flow; horizontal malaxer with heating & temperature display; inverter speed control; basic CIP wash kit | Small farms (~0.5-1 ton/day harvest); estate olive groves |
| Oliomio Gold | ~90-100 kg/hour | Enhanced automation (auto malaxer & drum washing, variable-speed feed auger)waste pump included; single or 3-phase | Medium farms (~0.8 ton/day); premium boutique mills needing labour-saving features |
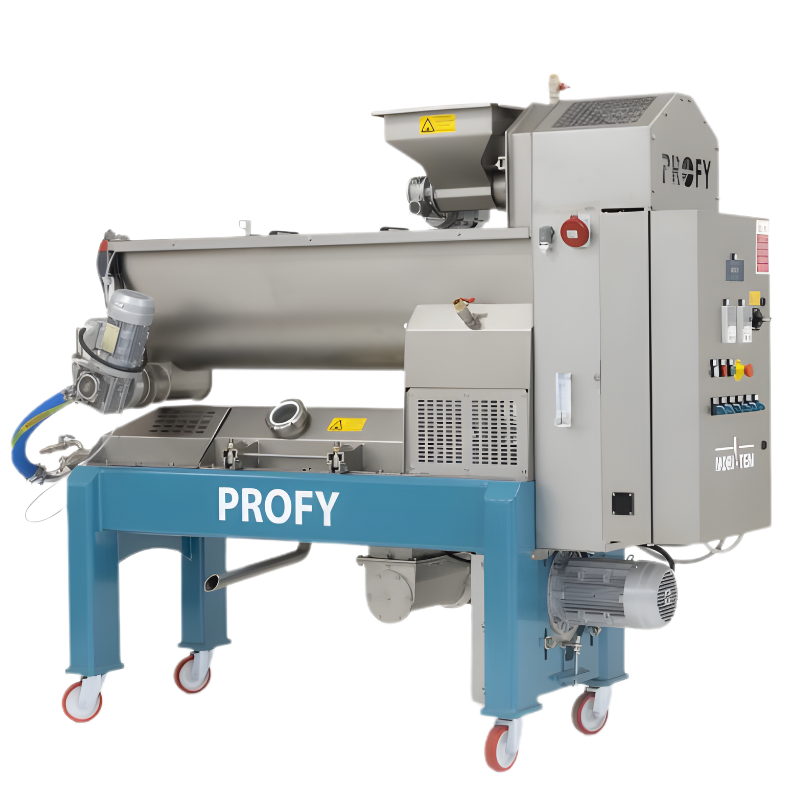
| Oliomio Profy 200 | ~150-200 kg/hour | Dual malaxers for semi-continuous processing; heavy-duty crusher; closed/vacuum malaxing; full automation; waste pump | Cooperative regional mills; small commercial processors (~1.5-2 ton/day) |
Table: Comparison of select Oliomio continuous mill models (MORI-TEM). All feature two-phase extraction, stainless steel construction, and integrated crushers and decanters; higher models add more automation and capacity. Note how the traditional press is absent - even the smallest Oliomio brings modern centrifugal extraction to the farm, highlighting the leap in technology from the old press or “monoblocco” mills of past decades.
For producers scaling beyond the monobloc units, MORI-TEM offers modular olive mill installations that handle larger throughputs while prioritising quality. These systems - marketed under names like Sintesi, Forma, Cultivar, and TecnoTEM Oliomio Sintesi Series - break the extraction process into separate machines (e.g., independent crusher, malaxer group(s), decanter, separator) designed to work in harmony. They introduce features like multiple malaxers for higher throughput, vacuum malaxation technology, and advanced control systems. Importantly, they still operate on the continuous two-phase principle and embody the same hygiene and automation ethos as the smaller Oliomio range. Here’s an overview of each series:
It is instructive to contrast the above Oliomio technologies with the outdated systems they have superseded - namely, the classic hydraulic press and early-generation farm mills (older “monoblocchi” units). Traditional olive presses involved grinding olives (often with stone mills) into paste, spreading that paste onto fibre mats, stacking them, and then applying tons of pressure in a press to squeeze out the oil/water mixture. This method, while romantic, had numerous drawbacks: it was labour-intensive and slow, exposed the olive paste to air for prolonged times, and was hard to keep clean. The mats and press equipment could harbour yeasts or moulds and were difficult to sanitise thoroughly. It was not uncommon for olives to begin fermenting in the interim between harvest and pressing - indeed, historical accounts describe farmers bringing sacks of olives to the mill that were “often already fermenting” by the time they were pressed. The result was oil of inconsistent quality and stability. Continuous centrifuge systems like Oliomio eliminated these problems by moving to an enclosed, stainless-steel process where olives are milled almost immediately after picking, drastically cutting the chance for fermentation or oxidation. The greater hygiene and speed of continuous extraction have improved average oil quality and made defects from processing (such as fusty or musty flavours from fermentation) much rarer in modern operations. As a report on introducing Oliomio technology in Australia noted, “centrifugal extraction…replaced older, labour-intensive systems with continuous-flow designs”, offering better hygiene, efficiency, and capacity - effectively rendering the old press method obsolete in quality-oriented production.
Early small-scale continuous mills (from the 1990s-2000s) were a huge step up from presses, but they lacked some refinements of today’s Oliomio models. For example, many older farm mills did not have automated temperature control for malaxation, nor continuous malaxer flow. The very first “Oliomio” monoblock (created by Tuscan innovator Giorgio Mori) was revolutionary for being compact and continuous, but subsequent generations have added further improvements. A comparison of features illustrates this evolution: the older Spremoliva 30 could only malax in batch mode (no simultaneous crushing while decanting) and had no heating system or temperature display on the malaxer. By contrast, an Oliomio 80 or Gold today has fully continuous malaxing with automated temperature control and readout. Earlier mills often used fixed-speed motors and one-size-fits-all settings, whereas new systems employ inverter drives and adjustable nozzles to accommodate different olive conditions (small, watery olives vs. large, fleshy ones, etc.). Another big leap is in automation: tasks like pomace removal and equipment washing, once manual, are now handled by integrated pumps and wash cycles in machines like the Gold and Profy. This not only reduces labour but also ensures more consistent cleanliness batch after batch. In terms of energy and water usage, modern two-phase decanters are also more sustainable - they eliminate the need for large volumes of dilution water required by traditional three-phase decanters (saving water and the energy to heat it) and produce a simpler waste stream (wet pomace) that can be repurposed or composted more easily than press liquor or black water from old systems.
Crucially, oil quality has improved with each technical advance. Traditional pressing often left higher sediment and water in the oil, necessitating longer settling or filtration and risking quicker oxidation. Continuous centrifugation yields cleaner oil immediately, and the lack of air contact preserves freshness. Chemical measures like peroxide value and UV stability are typically superior in oil produced by a modern continuous mill versus an old press, when starting with the same fruit. The ability to crush and extract within hours of harvest, at controlled temperatures, means free fatty acid levels stay extremely low and the positive flavour notes are maximised. Australian producers who have adopted the latest Oliomio systems consistently report better quality and consistency in their oils, even when processing smaller batches. As an example, Spring Gully Olives in Queensland upgraded to a two-phase Oliomio (150 kg/hr) and found it ideal: it allowed them to process their own crop and offer custom processing to neighbouring groves, all while producing oil that needed no further refining - “the 150 kg per hour Oliomio is an ideal capacity which allows small growers to have their own oil processed…and it leaves the oil in its natural state”. This kind of feedback underlines how modern machinery empowers even small-scale growers to achieve high extraction efficiency and premium quality that rivals the big producers.
In summary, the latest Mori-TEM Oliomio systems represent a convergence of advanced engineering and practical on-farm olive oil production. They enable professional, hygienic, and quality-focused extraction at scales from a few dozen kilograms up to several tonnes per hour. By carefully controlling each step - from fruit cleaning and crushing with minimal oxidation, to malaxation under controlled atmosphere, to efficient two-phase centrifuge separation - these machines ensure that the oil produced reflects the true potential of the olives. Australian growers using Oliomio equipment benefit not only from improved oil quality and shelf life, but also from greater independence and flexibility: they can harvest at optimal times and process immediately, rather than rushing to a distant community mill or risking fruit spoilage. The result is fresher, more flavorful extra virgin olive oil that meets the high standards of a sophisticated global market. And with the range of Oliomio models and configurations now available, producers can choose a setup tailored to their grove’s size and business model - whether it’s a one-person boutique press or a regional processing hub servicing multiple farms. The technology has truly opened a new chapter for the industry, one where tradition and innovation blend to produce the finest EVOO. Each bottle of oil pressed with these modern systems tells the story of careful harvest timing, immediate processing, and gentle extraction - a story that resonates strongly with Australia’s drive for quality and the world’s appreciation of premium extra virgin olive oil.

MARKET INSIGHT: GLOBAL OLIVE OIL ECONOMY 2023
Introduction
The global olive oil industry in 2023 has entered uncharted territory, experiencing an extraordinary surge in olive oil prices driven by a combination of climatic and economic forces. At the centre of this crisis lies Spain’s devastating drought, which has crippled the world’s largest olive oil producer. This severe shortage has led to a dramatic contraction in olive oil supply, triggering price escalation and a corresponding decline in consumer demand. The ripple effects are being felt worldwide, reshaping the balance between producers and consumers alike. Meanwhile, Australian olive oil producers find themselves in a rare position of advantage, benefitting from unprecedented market highs. This article explores the causes, consequences, historical trends, and economic signals surrounding this remarkable global olive oil price spike.
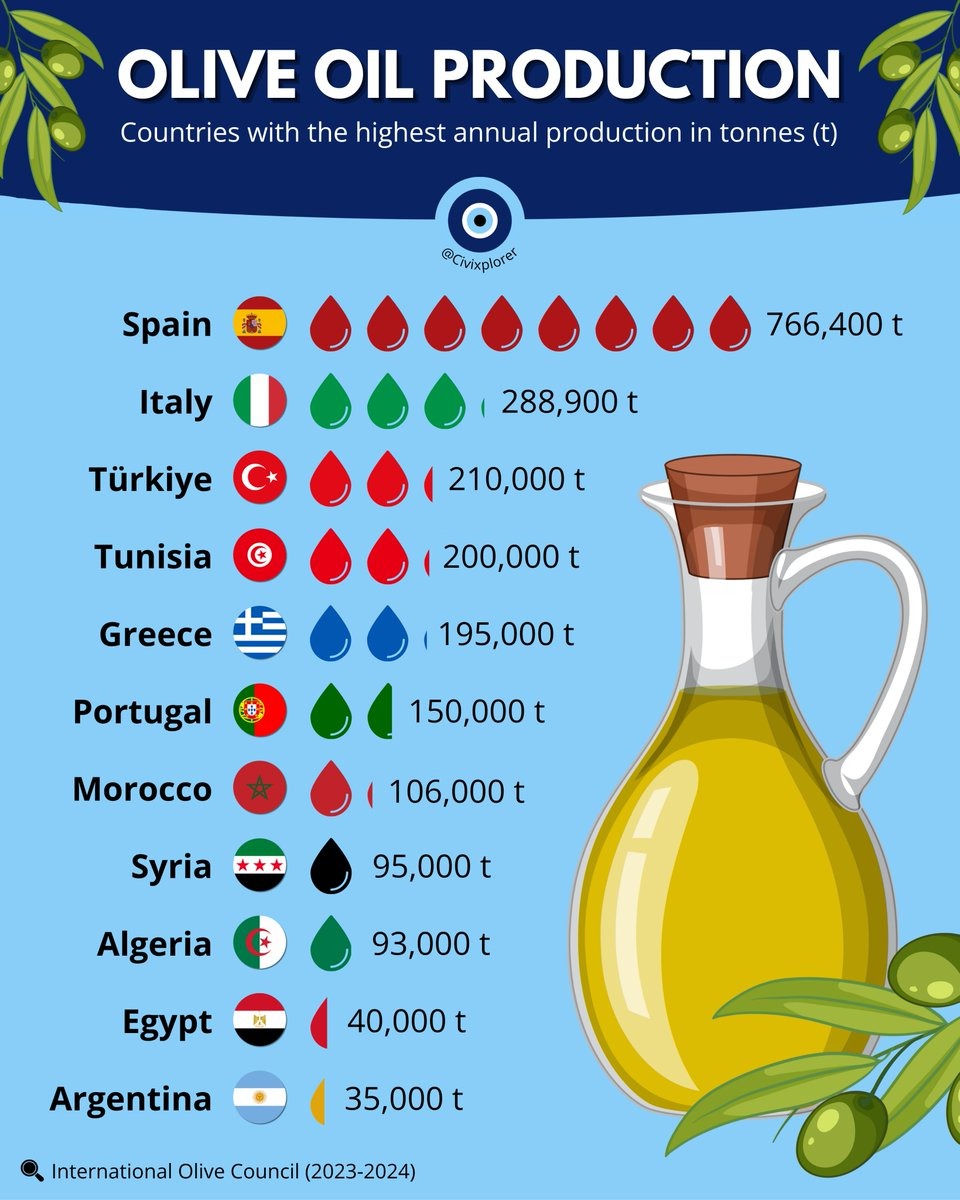
The ongoing drought across Spain stands as the principal factor behind the current olive oil price surge. As one of the largest olive oil-producing nations globally, Spain’s drastically reduced harvest - caused by months of extreme heat and minimal rainfall - has sharply curtailed olive oil availability in both European and international markets. This has intensified supply shortages, compelling consumers to pay more for what has long been a staple Mediterranean product. The interplay of limited supply and escalating demand has magnified price volatility, reinforcing the classic supply-and-demand imbalance now driving global markets.
Incredible to see the olive groves of Jaen, Spain. This one province produces around a fifth of the *entire* global supply of olive oil
— Secunder Kermani (@SecKermani) August 31, 2023
But a combination of drought & extreme heat has left many trees badly weakened... This years harvest looks set to be the worst in living memory pic.twitter.com/QYs41eXCwC
As prices have risen steeply, the shortage of olive oil has led to a noticeable decline in consumption, particularly in Spain, where demand has reportedly dropped by around 35%. Consumers are now scaling back their purchases, finding olive oil increasingly unaffordable compared to other cooking oils. The once-steady household consumption patterns are shifting as people seek alternatives or modify their cooking habits. This contraction in domestic demand not only highlights the growing accessibility gap for consumers but also underscores the broader economic strain caused by high inflation and food price increases.
Amid the turmoil, Australian olive oil producers are experiencing a windfall. Thanks to limited global supply, Australian growers are commanding record prices exceeding AUD $8 per litre, marking the highest levels ever recorded in the nation’s olive oil industry. This lucrative period presents a rare opportunity for Australian exporters, with demand from Europe - including Spain itself - now turning toward Australian supplies. For producers Down Under, this unique reversal of roles underscores how regional climate resilience and diversified production can translate into significant financial gains when global shortages arise.
The olive oil market’s volatility is not a new phenomenon. Previous spikes occurred in 1996, 2006, and 2015, each triggered by weather-related supply constraints. Yet, the 2023 price explosion stands out as the most dramatic in recorded history -over 40% higher than any previous price peak, and roughly double the magnitude of earlier surges. This extreme escalation reflects not just climatic hardship but a clear pricing bubble forming within the market, echoing the cyclical nature of commodity pricing.
The olive oil sector has long followed cyclical pricing patterns, typically alternating between low and high price phases roughly every decade. The current surge aligns almost perfectly with the predicted start of another 10-year cycle, occurring just three years into its anticipated timeline. Furthermore, a notable correlation has been identified between the Australian Food Inflation Index and the Global Olive Oil Price Index as reported by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). This connection illustrates the deep interdependence between food commodity pricing and global economic conditions.
While the IMF’s benchmark prices are denominated in USD, for the purposes of this analysis they have been converted to AUD to track the trend relative to Australian markets. These benchmark indicators -based on the world’s largest olive oil exporters -serve as a reliable gauge of overall market direction, confirming how global shortages and inflationary pressures move in tandem.
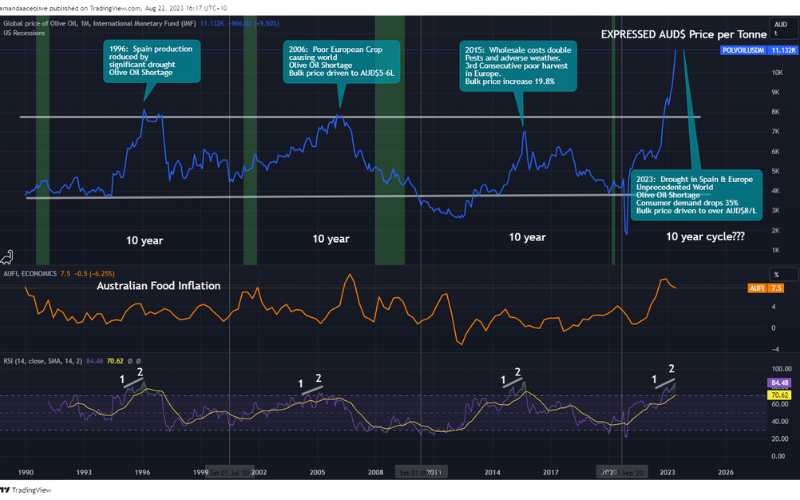 Global olive oil prices show a recurring 10-year cycle, driven by droughts, crop shortages, and rising production costs
Global olive oil prices show a recurring 10-year cycle, driven by droughts, crop shortages, and rising production costs
From a technical analysis perspective, the Relative Strength Indicator (RSI) is often used to measure price momentum and potential overextension in markets. On recent olive oil price charts, the RSI (represented in purple) indicates that prices have once again entered overbought territory - a level seen during previous speculative phases. Historically, such readings have preceded market corrections or reversals, suggesting that the current surge may not be sustainable in the long term.
Analysts caution that as the European olive harvest begins in September and October 2023, an influx of new oil supplies could help ease prices, though the timing and extent of this correction remain uncertain. Until then, speculative trading and limited inventory continue to support inflated market values.
The record-breaking olive oil prices of 2023, primarily triggered by Spain’s drought-induced production collapse, mark a turning point for the global olive oil economy. With consumer demand declining under the pressure of soaring prices and Australian producers thriving amid the scarcity, the industry is experiencing a dramatic rebalancing. Historical precedents, cyclical trends, and market indicators all point toward a complex, transitional period defined by volatility and uncertainty.
As the world’s producers, traders, and consumers adapt to these new market dynamics, one truth remains clear: olive oil - celebrated for its taste, health benefits, and cultural significance - continues to be at the mercy of both climate change and economic cycles. Stakeholders across the value chain must remain alert, flexible, and forward-thinking as the olive oil market navigates this extraordinary phase of transformation.
Other Sources